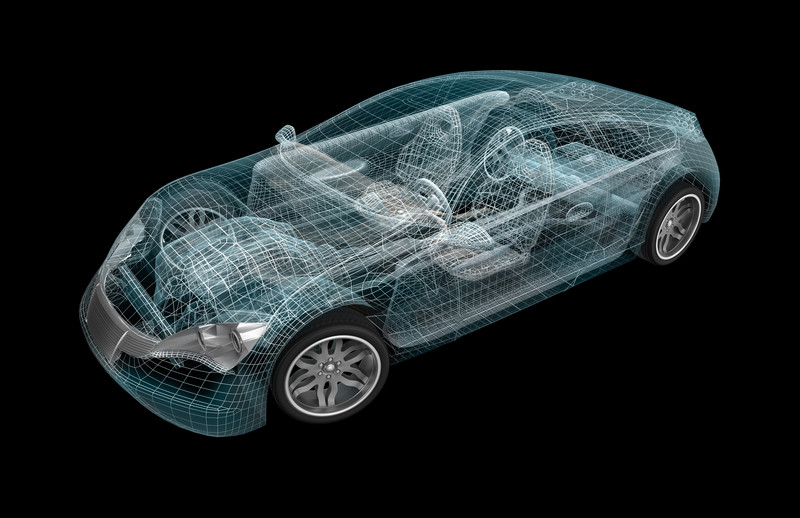
Design engineers are the minds behind the automotive technology and products that we use every day. When you choose a career in automotive design engineering you are not just choosing one specialty as a career choice. Underneath the hood, inside the doors and even underneath the vehicle hold examples of a design job for every engineering degree no matter what your specialty. If you are looking to become an automotive engineer, consider these design specialties from A to Z :
If any of these jobs pique your interest check out our 2-part post on the most critical skills you need to become an automotive design engineer (Here is Part 2)
Aerospace/Aeronautical Engineering
This engineering specialty may typically be associated with aircraft but they also have a very important function within automotive design. Aeronautical and aerospace engineers work with vehicle structures and aerodynamics and assist in designing vehicles with the least amount of wind resistance possible to reduce fuel consumption and make the vehicle more efficient. They work with the design teams and test concept vehicles to optimize how the vehicle will travel when it’s on the road.
Biological, Biomechanical and Biomedical Engineering
When you think of biological and biomedical engineering you may not realize they have a place in automotive design engineering. Passengers in a vehicle are living beings that have to interact with the vehicle and the vehicle must be designed for comfort and safety during normal use and for the potential of a vehicular accident. Both of these engineering fields work with the automotive design team to design comfortable seating for people of all sizes. They look at ergonomic issues, how people interface with the vehicle, and they study how test dummies react in a crash situation when an airbag is deployed. All of this testing and design must be done to launch the best possible vehicle to the market and garner the top safety awards that help to sell more vehicles. One of the key design focus areas in the automotive industry is the Human Machine interface and how it will impact the design of future vehicles.
Chemical Engineering
Chemical engineers have a place in the field of automotive engineers as they look at the design and performance of all the chemicals within the entire vehicle and their interactions. The automotive industry utilizes a reporting system called the International Material Data System (IMDS) which requires that all materials from every screw to a drop of adhesive be listed in the data system. Chemical engineers will review this data and search for alternatives if a restricted, banned, or potentially dangerous chemical is reported. There are requirements that all vehicles must meet for appropriate chemical levels within a vehicle which makes the IMDS system important.
Communications and Computer engineers
Communications and computer engineers are more involved in the cars of the future as they become integrated with computers. From the engine, to the onboard GPS and radio, all the components are now managed by computers and these computers must be networked so that they can communicate with each other to assist with on-board diagnostics.
 Electrical & Electromechanical Engineering
Electrical & Electromechanical Engineering
Electrical and electromechanical engineering are increasingly integral to the design of the next generation automobiles. In the old days, electrical engineers focused on simple circuits supply powers to lights, spark plugs and simple mechanical components in the vehicle. But now their role has expanded to designing detailed circuit boards that control the multitude of electronic components that make up modern vehicles. The role of electrical and electromechanical engineers continues to expand with the push to develop electric vehicles. This is being championed in the industry by the International Energy Agency electric vehicle initiative.
Environmental Engineers
Environmental engineers have become more common in the automotive industry as all industries push for ‘green designs’. These designs will reduce the impact of the vehicle on the environment through all its life phases from the design, production, driving, and disposal stages. Many environmental engineers also work in engine development to reduce emissions and to get those MPG numbers as high as possible, while saving mother earth.
Materials and Metallurgical Engineering
Materials and metallurgical engineers design and create new materials that will meet the needs of next generation vehicles. They create the materials and test them in the concept designs to determine if they will meet the performance requirements of the vehicle and improve the vehicle from generation to generation.
Mechanical Engineers
The real meat and potatoes of the automotive design engineering profession are the mechanical engineers who have their hand in all aspects of the vehicle design. Mechanical engineers will design, develop and test every part on the vehicle from the body components to the engine and controls. Mechanical engineers will work with mechanical models and determine stress points on the vehicle body that could cause unnecessary wear and tear on the vehicle. They work with crash dynamics allowing the vehicle to dissipate the force of a crash away from the occupants and prevent injury. No matter what function is being performed by the vehicle, mechanical engineers have a role in designing and testing it.
Optical Engineering
A little known field of automotive engineering is optical engineering. Within the vehicle we have several systems that must be illuminated for visibility when driving at night. In order to evenly light these systems, optical engineers employ several strategies to spread and diffuse light so that it will be displayed evenly to the driver and passenger for easy viewing.
Plastics Engineers
As vehicles evolve, the demand is there for lighter materials both for the interior and the engine compartment. This is where plastics engineers join the automotive design team. Plastics engineers help to identify new materials that can be used in innovative ways to reduce the weight of a vehicle and help to improve fuel efficiency.
Power Train Engineers
Power train engineers get to the root of the automotive design and work from the engine through the transmission, to where the wheels hit the road and propel the vehicle forward. These engineers design everything from the high power sports car with the turbo charged high torque power trains to the highly efficient electric vehicles on the road today.
Software and Systems Engineers
In the old days automobiles were more mechanically based. With some general tinkering problems could be fixed by most backyard mechanics. Those days are long gone and now vehicle issues are diagnosed via an on board diagnostics (OBD) computer system that is run by a custom developed software and integrated into the entire vehicle computer system. OBD is required on all vehicles from 1996 on and regulated by the US Environmental Protection Agency. Troubleshooting vehicles now requires plugging a hand held computer into the OBD port and running a program that generates error codes. The program also helps in determining and completing vehicle repairs. Software and systems engineers are the ones who design this functionality into the vehicles on the road today.
Thermal Engineers
In the old days vehicle cooling systems were centered on a radiator and when vehicles were stuck in traffic jams there was always the possibility of a vehicle overheating. Thermal engineers have developed new methods and materials that help improve airflow and heat dissipation in the vehicle’s engine compartment making over-heating a thing of the past – even when operating in the most stringent conditions. Thermal engineers are responsible for working with the engineering team to make sure that all designs operate in the most efficient, yet comfortable way possible.
These are some of the engineering specialties that have roles in the development of the next generation automobiles. No matter what your engineering degree, there is a place for you in automotive design engineering!

Comments 1
Interesting reading on all that goes into making cars. What I was looking for, which this article gave me insight to, just not specifics, was the tinting of the windows on vehicles today. Personally, it seems that concept has gone too far because we now see driver side windows so dark, you can’t see the face of the driver! I was looking for the “Why” those windows have become so dark and “How did it become legal?”.